KEY LARGO, Fla. — Comfortable clothes are emerging as a source of plastic that’s increasingly ending up in the oceans and potentially contaminating seafood, according to Gulf Coast researchers who are launching a two-year study of microscopic plastics in the waters from south Texas to the Florida Keys.
The project, led by the Mississippi-Alabama Sea Grant Consortium, will rely partly on volunteers in coastal cleanup events. It also will expand a year’s worth of data collected around Florida that predominantly found microfibers – shreds of plastic even smaller than microbeads flowing down bathroom sinks and shower drains.
Yoga pants, fleece jackets, sweat-wicking athletic wear and other garments made from synthetic materials shed microscopic plastic fibers – called “microfibers” – when laundered. Wastewater systems flush the microfibers into natural waterways, eventually reaching the sea.
“Anything that’s nylon or polyester, like the fleece-type jackets,” University of Florida researcher Maia McGuire said.
When McGuire set out to study the kinds of plastic found in Florida waters, she expected to mostly find microbeads – the brightly-colored plastic spheres the U.S. government banned from rinse-off cosmetic products in 2015 because of the potential threat to fish and other wildlife.
Instead, McGuire predominantly found microfibers, even smaller than microbeads and coming from places most people don’t consider dangerous to marine life: their closets.
“I totally thought we were going to be finding microbeads and (bigger) fragments,” McGuire said. “What do we do about it is the multimillion dollar question. The consensus seems to be that we need improvement in technology in washing machines and wastewater treatment plants in combination in order to try and filter out these fibers. There’s just so much we don’t know.”
Studies of the Great Lakes and New York Harbor and surrounding waterways found high concentrations of plastics pollution, including microbeads. McGuire’s data from Florida waters, compiled from 1-liter samples run through filters fine enough to catch microfibers missed by the trawls used in the larger studies, adds to the growing research focused on plastic pieces that degrade but never disappear.
The Gulf Coast study will use McGuire’s methodology to determine the prevalence of microfibers and other microscopic plastics.
A plastic “garbage patch” like one circulating in the Pacific Ocean is unlikely in the Gulf of Mexico, but the regional study may reveal areas particularly prone to the accumulation of plastics, said Caitlin Wessel of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s Marine Debris Program.
“There hasn’t been a lot of baseline study covering microplastics, and the studies that have been done haven’t been as wide-reaching,” Wessel said. “We’re hoping to use the data as a baseline, but also find sources of microplastics and find out what types of microplastics are the biggest issue in the Gulf.”
It’s not yet known how much microfibers hurt the health of marine animals that ingest them, or whether their accumulation up the food chain is harmful.
“The big concern is we know the amount of plastic in the ocean is increasing, and increasing somewhat exponentially at this point,” McGuire said. “It’s got chemicals in it, chemicals stick to it, animals eat it. We know a lot of the larger animals have impacts from larger plastics, so we think there’s an effect on smaller animals (from microplastics).”
The emerging data has prompted clothing company Patagonia – which makes fleece jackets and other apparel from synthetic materials – to support research into the prevalence of microfiber pollution and promote information for consumers about ways to minimize microfiber shedding in laundry.
Consumer-focused efforts such as Patagonia’s outreach, liquor giant Bacardi’s decision to stop adding plastic straws and stirrers to cocktails at company events, Miami Beach’s ban on Styrofoam containers or the federal microbeads ban can help slow the rate of microfibers and other plastics adding up in the oceans, but the pollution also needs to be addressed at its source and at wastewater treatment plants, Wessel said.
McGuire’s Florida Microplastic Awareness Project from September 2015 to August 2016 analyzed samples collected by volunteers from 256 sites around the state’s peninsula and the Florida Keys. Eighty-nine percent contained at least one piece of plastic.
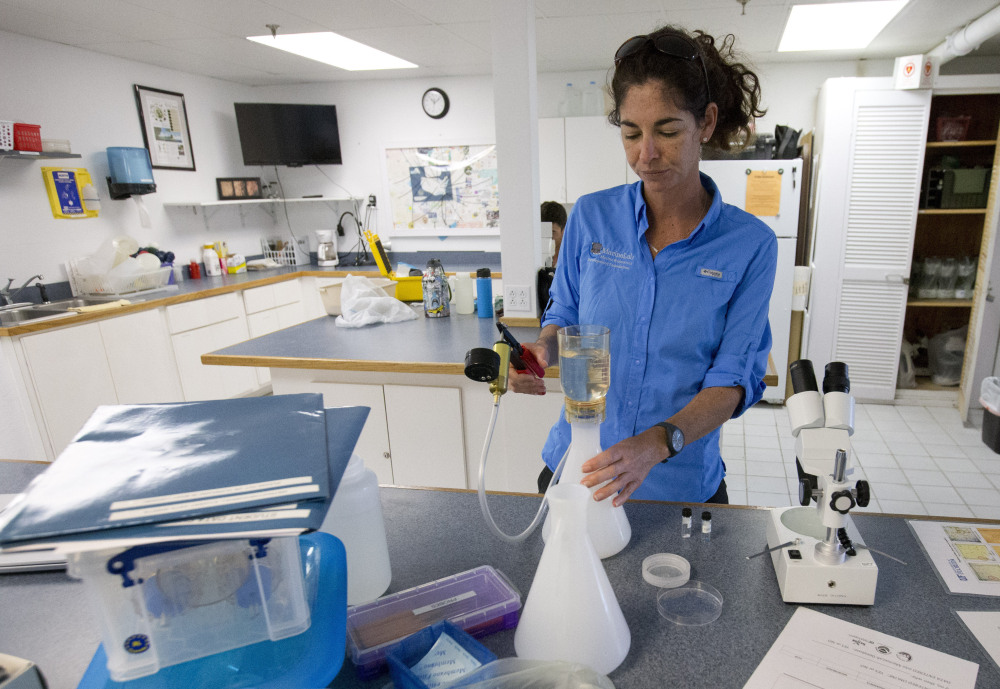
Microfibers comprised the vast majority of plastic found – 82 percent.The samples sent to McGuire were similar to one collected in early February by Sarah Egner, director of research and curriculum development at MarineLab in Key Largo. She waded knee-deep off a boat ramp into Largo Sound, and on a sunny day the water seemed clear in her white plastic bottle. Under a microscope in her laboratory, however, two dark threads seemed to swim among red and green plankton — two microfibers.
Send questions/comments to the editors.