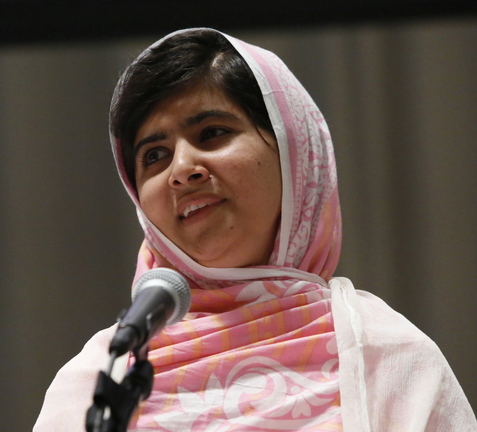
In one short year, Malala Yousafzai has transformed herself from obscure Taliban victim to an internationally celebrated model of courage in defense of human rights.
Founder of the nonprofit Malala Fund that advocates for girls’ education and raises money for schools and tuition in her native Pakistan, Malala has used her place on the world stage to declare personal victory over terrorism and to call for peace talks with the Islamic extremists who attacked her.
Her activism in defiance of renewed death threats has, in the estimation of prominent media and human rights organizations, put her in the running for the Nobel Peace Prize that is to be awarded Friday. If the prestigious award is bestowed on 16-year-old Malala, she would be the youngest peace laureate in Nobel history.
Taliban gunmen boarded her school bus on Oct. 9, 2012, and shot her in the head for denouncing their attempts to return her Swat Valley homeland to the social mores of the Middle Ages. Girls’ education was banned, women were beaten for leaving their homes without a male relative escort, and the central square of Malala’s hometown, Mingora, became a place of flogging and execution.
Malala was airlifted to Britain after the attack and spent months in a Birmingham hospital being treated for her injuries.
Once recovered, Malala stepped back into the public eye with ardent speeches in support of equal rights for girls and education for all. She kicked off her reinvigorated activism with an address to 1,000-plus youth delegates to the United Nations in July, when she declared books and pens “our most powerful weapons.”
A Taliban spokesman, Shahidullah Shahid, told news agencies in Pakistan that Malala was shot for defaming Islam, not for her outspoken support for girls’ education, and that the group would try to attack her again.
Send questions/comments to the editors.