SIOUX FALLS, S.D. – The pipe organ has ruled the Christian worship sanctuary for centuries, and the majestic instrument continues to reign supreme in many Roman Catholic and mainline Protestant parishes.
It’s a tougher sell for congregations moving toward contemporary worship.
The growth in praise-band led services, combined with a nationwide shortage of qualified organists, is prompting many congregations to leave pipe organs out of their new construction plans.
Jerry Aultman thinks that’s a mistake.
The longtime organist and music professor at Southwestern Baptist Theological says the pipe organ doesn’t need to be relegated to funerals and weddings, and it fits nicely into modern worship when used in the right way.
“We shouldn’t abandon the organ in contemporary music styles,” said Aultman, who plays each Sunday at First Baptist Church in Dallas. “The organ is a wonderful instrument to blend in with any kind of instrumental ensemble. It can fill in a lot of holes in the sound.”
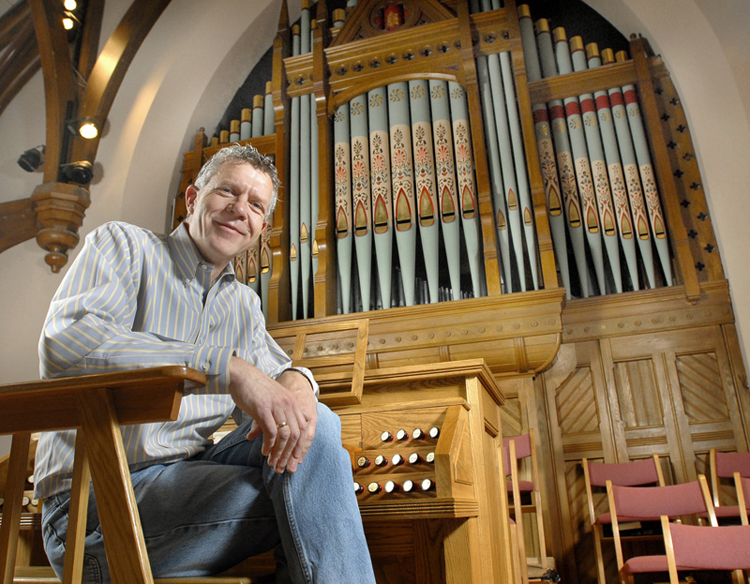
The pipe organ, which dates back to the third century B.C., “has always been the choice for churches who want one musician to fill the room with sound,” South Dakota organ builder John Nordlie said.
The instrument has been considered expensive throughout its history, with current prices ranging from $100,000 to well into the millions. But pipe organs hold their value and can last for generations if they’re well-designed and well-maintained, he said.
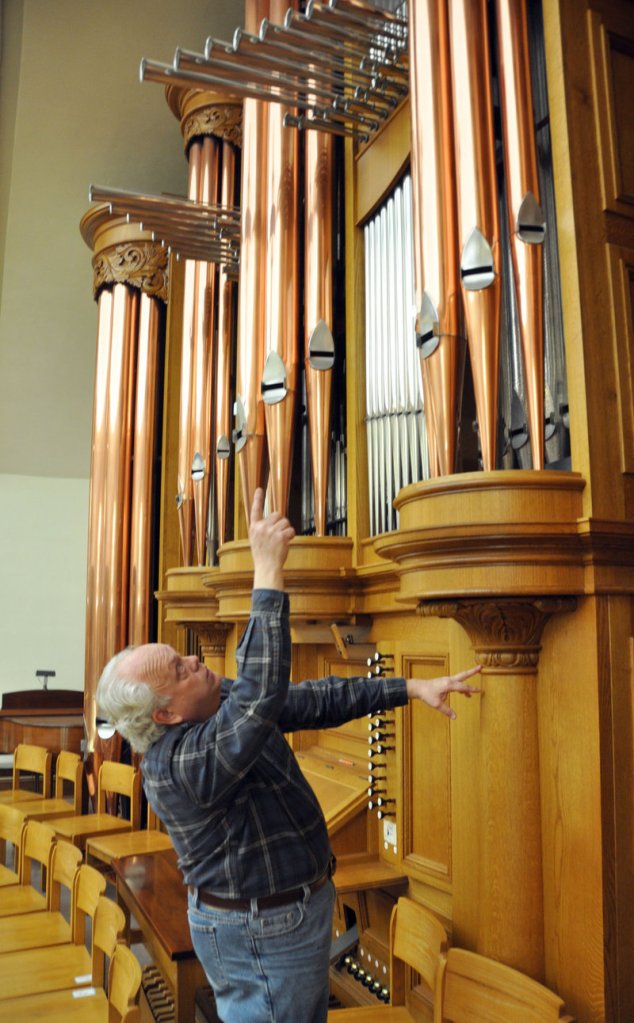
Nordlie crafted his first instrument in 1977 for a church in Appleton, Minn., and has built nearly 50 organs in his Sioux Falls shop. Each part is handcrafted, from the wood and metal pipes that turn airflow into notes to the ornate cabinetry that houses the massive structures.
Although electronic and digital instruments can try to emulate the sound of wind being pushed through pipes, “they will never match the sound of the pipe organ,” Nordlie said.
“The difference is there,” he said. “Whether you take the time to listen carefully is entirely up to you.”
The large megabuilders of the 1960s have largely disappeared, but numerous smaller companies are building as many instruments as they can turn out, says James Weaver, executive director of the Organ Historical Society.
Weaver says music aficionados still value the incredible amount of craftsmanship put into each organ. For proof, he points to the top-of-the line organs being built for municipal concert halls such as the Meyerson Symphony Center in Dallas, the Kimmel Center for the Performing Arts in Philadelphia and Walt Disney Concert Hall in Los Angeles.
“The idea of a handmade instrument is something which is just still quite a wonderful thing in our society and it’s something that we really care about,” Weaver said.
Another factor contributing to the organ’s decline is a fewer number of musicians qualified to sit behind the consoles. The pipe organ is a complex instrument, and playing it well requires intensive training and practice.
Weaver says the number of organ students dropped tremendously a few years ago as musicians worried about whether their degrees would lead to jobs. He’s starting to see a turnaround. “Now there are more positions available I think,” he said.
Aultman says there are fewer universities offering organ degrees, but the ones that remain are stronger.
“There are still students that are majoring in organ, and there are still churches that will hire them and pay them a living wage,” he said. “And I think that’s just going to get better.”
Aultman urges organists who want to make a living to embrace contemporary styles. He suggests that organists trained to play only off sheet music learn to play off chord charts like Nashville studio musicians.
“My advice to organists is, ‘Don’t be a snob,’ ” he said. “You’re not going to probably find a position where you can play all Bach preludes and fugues for the bulk of your work.”
Send questions/comments to the editors.